
argo template示例
1.simple template example
示例1:基础template(永远的hello world)
使用一个简单的argo template,创建一个容器,使用docker中最新whalesay镜像。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow # new type of k8s spec
metadata:
generateName: hello-world- # name of the workflow spec
spec:
entrypoint: whalesay # invoke the whalesay template
templates:
- name: whalesay # name of the template
container:
image: docker/whalesay
command: [cowsay]
args: ["hello world"]
resources: # limit the resources
limits:
memory: 32Mi
cpu: 100m
在这个template中,argo为k8s添加了一个为workflow的新的kind,上面的adsl包含一个名为whalesay的模板,该模板运行docker / whalesay容器并调用Cowsay的“ hello world”。 entrypoint:指定Kubernetes执行工作流规范时应该调用的初始模板。当有多个template时可以显示的声明调用入口使用的模板。
示例2:带参数的template
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: hello-world-parameters-
spec:
# invoke the whalesay template with
# "hello world" as the argument
# to the message parameter
entrypoint: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: hello world
templates:
- name: whalesay
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message # parameter declaration
container:
# run cowsay with that message input parameter as args
image: docker/whalesay
command: [cowsay]
args: [""]
这个template在上面的hello world基础上作了一点调整,在示例1中args是固定写死的,示例2中将给定inputs参数,使得template支持输入参数。 arguments.parameters:给定了字段名为message的参数,默认值为hello word。 spec.arguments.parameters中的参数作用域是全局的,可以通过方式访问 template中cowsay使用inputs的参数message,参数必须使用双引号括起来以转义yaml中的大括号。 argocli可以指定input的参数值,这点是kubectl无法支持的。
1
2
argo submit arguments-parameters.yaml -p message="goodbye world" # 将"goodbye world"赋值给message
argo submit arguments-parameters.yaml # message使用默认值
同时argocli也支持使用json文件或者yaml文件配置参数,当需要给定多个参数时可以使用这种方式
1
2
3
4
5
params.yaml文件中配置message的值,yaml文件内容如下:
message:goodbye world
-----------------------------------------------
argo submit arguments-parameters.yaml --parameter-file params.yaml // argo命令,使用params.yaml文件给定参数
spec.arguments.parameters中的参数作用全局,可以在steps中调用
下面示例中,在不手动指定参数时,流程A和流程B都默认使用全局参数log-level。而不用在多个steps中多次配置,只需引用全局参数即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: global-parameters-
spec:
entrypoint: A
arguments:
parameters:
- name: log-level
value: INFO
templates:
- name: A
container:
image: containerA
env:
- name: LOG_LEVEL
value: ""
command: [runA]
- name: B
container:
image: containerB
env:
- name: LOG_LEVEL
value: ""
command: [runB]
示例3:任意组合template
argocli支持在不改变template的内容上任意组合你需要调用的执行入口模板和输入参数。通过entrypoint 和p参数,一个指定调用入口模板,一个指定输入参数。 命令行参数还可以用于覆盖默认入口点并调用任何模板在工作流规范。例如,如果你添加一个新版本的whalesay模板称为whalesay-caps但你不想改变默认入口点,你可以从命令行调用这个如下
1
2
# 执行示例3的template,执行时修改entrypoint为whalesay-caps和指定参数message="goodbye world,但不会改变template的内容
argo submit arguments-parameters.yaml --entrypoint whalesay-caps -p message="goodbye world"
2.argo steps adsl example
示例1:分步template
argo template可以通过steps控制模板执行顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: steps-
spec:
entrypoint: hello-hello-hello
# This spec contains two templates: hello-hello-hello and whalesay
templates:
- name: hello-hello-hello
# Instead of just running a container
# This template has a sequence of steps
steps:
- - name: hello1 # hello1 is run before the following steps
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "hello1"
- - name: hello2a # double dash => run after previous step
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "hello2a"
- name: hello2b # single dash => run in parallel with previous step
template: whalesay
arguments:
parameters:
- name: message
value: "hello2b"
# This is the same template as from the previous example
- name: whalesay
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message
container:
image: docker/whalesay
command: [cowsay]
args: [""]
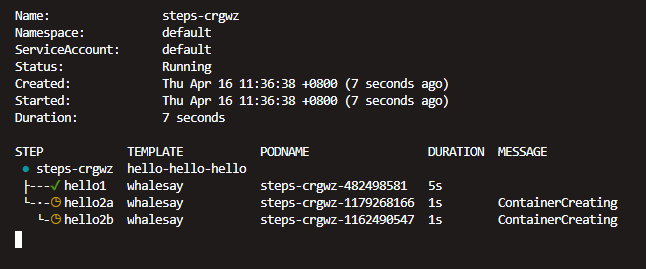
上面的示例中,template:hello-hello-hello定义了steps,执行步骤:
- hello2a和hello2b依赖于hello1,优先执行hello1,hello2a,hello2b等待
- 等待hello1执行完成后,hello2a和hello2b并行执行,没有依赖关系
使用watch查看执行过程,和如上所述一致
示例2:DAG(有向无环图) template
基于指定步骤序列的替代方法,可以通过指定每个任务的依赖项将工作流定义为定向无环图(DAG)。对于复杂的工作流,这可以更简单地维护,并允许在运行任务时实现最大的并行性。 dag执行成功/失败逻辑规则有两种,由FAILFAST标签控制,默认为true,可以人为手动改变。
- true,只要dag其中一个节点执行执行失败,就不再继续执行后续节点,等待当前所有正在执行的节点执行结束后直接返回失败。
- false,子节点中执行失败也会继续执行,直到所有可以执行的节点都执行完毕后返回失败。
```yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: dag-diamond-
spec:
entrypoint: diamond
templates:
- name: echo
inputs:
parameters:
- name: message container: image: alpine:3.7 command: [echo, “”]
- name: diamond
dag:
tasks:
- name: A template: echo arguments: parameters: [{name: message, value: A}]
- name: B dependencies: [A] template: echo arguments: parameters: [{name: message, value: B}]
- name: C dependencies: [A] template: echo arguments: parameters: [{name: message, value: C}]
- name: D
dependencies: [B, C]
template: echo
arguments:
parameters: [{name: message, value: D}]
```
上面的示例定义了A,B,C,D四个steps,diamond中B,C 依赖由dependencies定义,需要依赖A,D需要依赖B,C。这个DAG的工作流为:
- 首先执行A
- 等待A执行完成后,B,C并行执行
- 等待B,C都执行完成最后执行D 这个示例中只有一个跟节点A,每个节点都是一个simple template。复杂的argo dag template中可以有多个跟节点,并且每个节点可以是一个复杂的template,比如steps template,dag template等。也就是说,支持一个复杂的template拆分为多个template。
- name: echo
inputs:
parameters:
示例3:制作工件
argo可以支持将节点制作成工件持久化存储在工件库中,之后可以当做元件直接使用。首先需要为argo添加元件库存储服务配置,一般有aws s3,minio,gcs等可选。 元件库配置参考:argo 元件库配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: artifact-passing-
spec:
entrypoint: artifact-example
templates:
- name: artifact-example
steps:
- - name: generate-artifact
template: whalesay
- - name: consume-artifact
template: print-message
arguments:
artifacts:
# bind message to the hello-art artifact
# generated by the generate-artifact step
- name: message
from: ""
- name: whalesay
container:
image: docker/whalesay:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["cowsay hello world | tee /tmp/hello_world.txt"]
outputs:
artifacts:
# generate hello-art artifact from /tmp/hello_world.txt
# artifacts can be directories as well as files
- name: hello-art
path: /tmp/hello_world.txt
- name: print-message
inputs:
artifacts:
# unpack the message input artifact
# and put it at /tmp/message
- name: message
path: /tmp/message
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["cat /tmp/message"]
这个工作流template包含两个按顺序运行的步骤。第一步是generate-artifact(生成工件),它将使用whalesay模板生成工件,并由第二步称为print-message(打印消息)使用,然后使用生成的工件。
3.argo conditionals&loops&recursion adsl example
关于argo的条件判断与循环
示例1:argo conditionals
argo提供when关键字用来声明条件判断,好像只支持==和!=两种
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: coinflip-
spec:
entrypoint: coinflip
templates:
- name: coinflip
steps:
# flip a coin
- - name: flip-coin
template: flip-coin
# evaluate the result in parallel
- - name: heads
template: heads # call heads template if "heads"
when: " == heads"
- name: tails
template: tails # call tails template if "tails"
when: " == tails"
# Return heads or tails based on a random number
- name: flip-coin
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import random
result = "heads" if random.randint(0,1) == 0 else "tails"
print(result)
- name: heads
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was heads\""]
- name: tails
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was tails\""]
上述示例,模板flip-coin首先在heads和tails之间随机选取,随机结果时heads时调用模板heads,随机结果是tails时调用模板tails
示例2:argo loops
argo提供withItem和withParam进行迭代操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# withItem迭代对象
# 该示例迭代一个列表,以image: tag的形式打印输出
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: loops-maps-
spec:
entrypoint: loop-map-example
templates:
- name: loop-map-example
steps:
- - name: test-linux
template: cat-os-release
arguments:
parameters:
- name: image
value: ""
- name: tag
value: ""
withItems:
- { image: 'debian', tag: '9.1' } #item set 1
- { image: 'debian', tag: '8.9' } #item set 2
- { image: 'alpine', tag: '3.6' } #item set 3
- { image: 'ubuntu', tag: '17.10' } #item set 4
- name: cat-os-release
inputs:
parameters:
- name: image
- name: tag
container:
image: ":"
command: [cat]
args: [/etc/os-release]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# withParam迭代参数
# 该示例在对模板gen-number-list输出的seconds参数列表进行迭代,由模板sleep-n-sec调用执行打印每次迭代的seconds的值并执行sleep
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: loops-param-result-
spec:
entrypoint: loop-param-result-example
templates:
- name: loop-param-result-example
steps:
- - name: generate
template: gen-number-list
# Iterate over the list of numbers generated by the generate step above
- - name: sleep
template: sleep-n-sec
arguments:
parameters:
- name: seconds
value: ""
withParam: ""
# Generate a list of numbers in JSON format
- name: gen-number-list
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import json
import sys
json.dump([i for i in range(20, 31)], sys.stdout)
- name: sleep-n-sec
inputs:
parameters:
- name: seconds
container:
image: alpine:latest
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo sleeping for seconds; sleep ; echo done"]
示例3:递归调用
我们可以对示例1进行一点改进,示例1中当满足wen条件时,调用的template是template本身,若将其改为上层template节点,那么就复合递归的结构,当然使用递归的时候你必须确保拥有结束条件,不会造成死循环。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 当 == tails,将继续执行template flip-coin,直到 == heads才会结束
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: coinflip-
spec:
entrypoint: coinflip
templates:
- name: coinflip
steps:
# flip a coin
- - name: flip-coin
template: flip-coin
# evaluate the result in parallel
- - name: heads
template: heads # call heads template if "heads"
when: " == heads"
- name: tails
template: flip-coin # call tails template if "tails"
when: " == tails"
# Return heads or tails based on a random number
- name: flip-coin
script:
image: python:alpine3.6
command: [python]
source: |
import random
result = "heads" if random.randint(0,1) == 0 else "tails"
print(result)
- name: heads
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was heads\""]
- name: tails
container:
image: alpine:3.6
command: [sh, -c]
args: ["echo \"it was tails\""]